I have been meaning to write this blog for some time now but somehow kept on postponing (read procrastinating...). I read about this technique of Consistent Hashing a while back and was mesmerized by its elegance. Recently read it again in this brilliant blog and thought of expressing it in my own words for posterity. So let us begin.
Hashing
I won't talk too much about hashing since it is a very basic computer science concept. In a word, it means mapping an object to another object. Or more generally, mapping a key to a value where their types don't matter. Mostly the mapping is from a string to int.
There could be multiple different hash functions that can exist which randomize the how the keys are hashed to the values. We are going to consider a simple use case where let's say you have N different servers and there are multiple keys that you want to distribute among those servers. How do you do it?
Well, a simple strategy is that you have a function which applies some logic to map the keys to an integer value. So, f(key) = some integer value, say val. And now since there are N servers we have to distribute them to, we can take val%N which will give us an integer in [0, N - 1] and based on the result we can send the key to the corresponding server.
This works out pretty well if the number of servers remain constant (i.e N). However, we know that when dealing with distributed systems, assuming the servers won't go down is pretty unreasonable. Also, in many cases you may want to add more servers to handle more traffic so the number of servers can go up as well as go down.
If we use the same approach (taking %N) as above, each time the number of servers change, we will have to re-hash all the keys with the new number of servers available. This would lead to a lot of unnecessary moving around of keys across the servers. This would also break any local caching present on the servers. This is actually one of the problems faced by distributed databases.
Hence we want to find out a solution where if the number of servers change, we don't have to rehash a large number of keys. This is where consistent hashing comes into the picture.
Consistent Hashing
The concept of consistent hashing is very straightforward, and it has to do with circles. Basically, if we can map our keys as well as servers on a ring, consistent hashing claims that we can solve the re-hashing problem in case the servers go up or down.
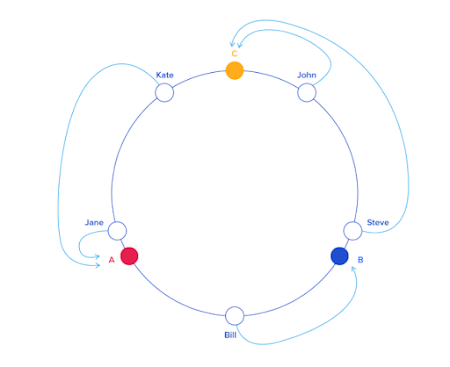
Let us assume that we have three servers - A, B and C. Also say we have five keys, John, Steve, Bill, Kate and Jane. For doing consistent hashing, we need to map all these entities on to a ring. A simple way to do that is to define a function f such that f(key) = theta (where 0 <= theta <= 360). So now theta can be considered as an angle and therefore can be mapped onto a circle.
Applying the above strategy here is how the keys will look like after the mapping:
And once everything is mapped, we define a simple rule that a key would belong to the server which is closest to it in the anticlockwise (or clockwise, doesn't matter) direction. So based on this rule it is easy to see that John maps to server C, Bill maps to B, Jane maps to A and so on.
Why is this beneficial you ask? Well let's consider a server goes down. Say server B in the diagram above. How many keys will be shifted? Only those that were mapped to B. In this case that is only 1. Bill will now map to server C (closest anticlockwise in the new setup) instead of B.
This was a small example, but even with a large number of keys, with a good distribution, the number of keys that will have to be shifted would be very less in comparison to our %N approach.
Moreover, this mapping on a ring strategy allows us to incorporate the server capacity into consideration in a very cool way. Let's say some servers are bigger than other servers and can handle more keys. All we need to do is create more copies of that server on this ring. So for eg. if server A can handle twice the load than server B, we can create two copies of A, say A0 and A1 and map both of them to the ring. It is easy to see that with random distribution the number of keys mapped to A (A0 + A1) will be twice as many mapped to B.
Use Case
Consistent hashing is an incredibly useful technique and used across various distributed systems. Known examples of consistent hashing use include (from wikipedia):
- Couchbase automated data partitioning
- Partitioning component of Amazon's storage system Dynamo
- Data partitioning in Apache Cassandra
- Data partitioning in Voldemort
- Akka's consistent hashing router
- Riak, a distributed key-value database
- Akamai content delivery network
- Discord chat application
Comments
Post a Comment